|
Magnestism
|
|
|
| Solutions |
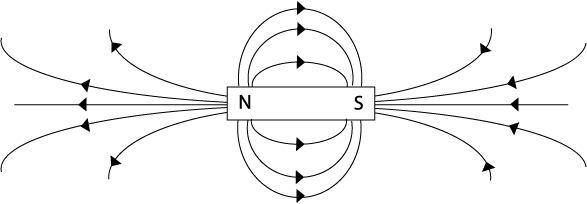
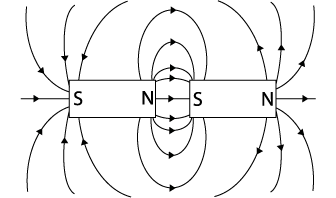
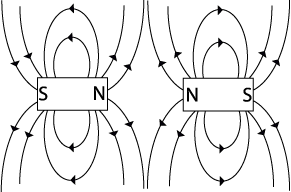
Q2: Draw the observed field between two magnets in two different configurations.
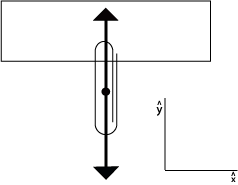
Q3: Draw a free body diagram for the steel paper clip.
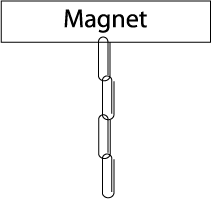
Q4: If the paper clip shown has a mass of 1.45g, what must be the minimum upward magnetic force upon it? F = ma 1.45g x 9.8m/s2 = 14.2 N Q5: Which substances do and do not effect the field and how? None of the substances listed should affect the magnetic field. Q6: How can you use a second magnet to increase this number (sketch this)?
Q7: Starting from contact, slowly remove the magnet to a distance of 1 cm. Describe what you observe. Removing the magnet from the top paper clip a distance of 1 cm has no affect on the chain of paper clips, due to the fact that the magnetic field is still is still acting on the top paper clip. Q8: With a drawing explain this phenomenon in terms of lines of magnetic field
Q10: How do these fields compare to the electric fields you have studied? The magnetic fields are similar to electric fields. With electricity, opposite charges attract (+ and -) and alike charges repel (+ and +)(- and -). Magnetism is similar to electricity in that opposite poles attract (N and S) and alike poles repel (N and N)(S and S). |
|
|
|
|